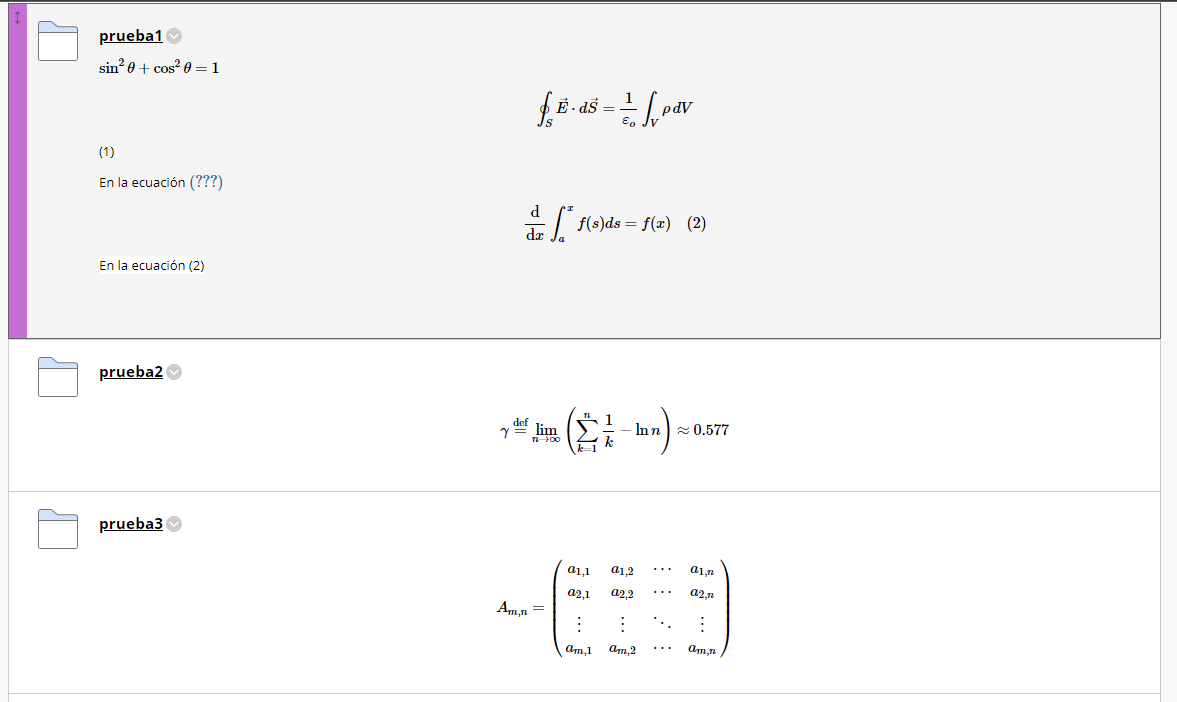Contents
Learning Goals
The learning goals for this module include:
- Learn about the LaTeX support provided by environments like GeoGebra, Brightspace, and Google Docs.
- Learn how to include LaTeX on any webpage using the MathJax Javascript library.
- Explore other platforms that offer LaTeX support.
Before You Start
Think of a few different document types or platforms that you use to communicate mathematics. This might include word-processors, slide-presentation software, online learning environments, webpages, graphing calculators, etc. How many different tools do you need to use to insert mathematical expressions and symbols into these environments?
LaTeX Everywhere
The LaTeX support included in various digital platforms allows you to use LaTeX or LaTeX-style commands to include mathematics without having to create an entire LaTeX document. In most chases, there are facilities on these platforms to inject a small amount of LaTeX (just what you need) into your document or page.
LaTeX in GeoGebra
The free online graphing and geometry tool GeoGebra includes LaTeX support in its text tool, allowing you to include LaTeX-based formulas on graphs and sketches that you create.
Try out the GeoGebra support for LaTeX following these steps:
- Go to the GeoGebra graphing calculator page.
- Select the Tools menu and choose the Text Tool within the Media Tools category.
- Click on the graphing area to bring up the Text Tool, and select LaTeX Formula.
- Enter one of the LaTeX commands you have learned.
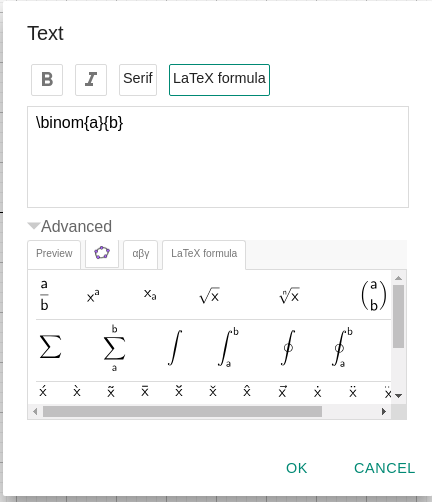
Read more about GeoGebra's LaTeX support on the GeoGebra wiki.
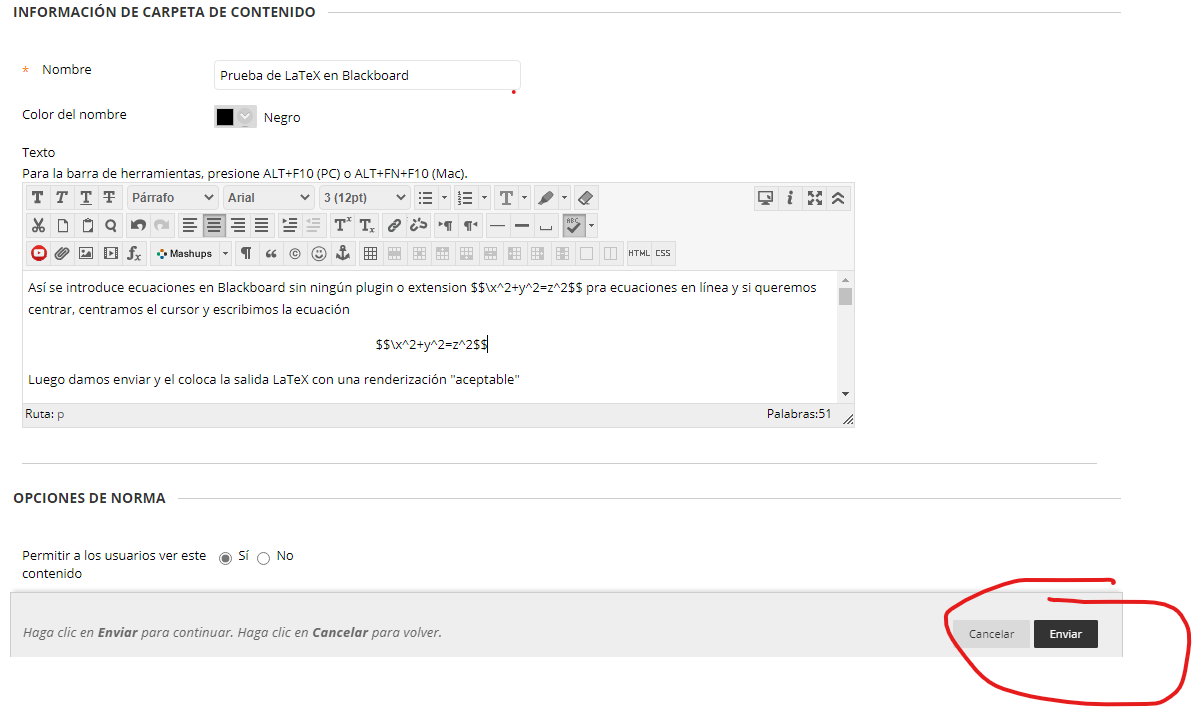
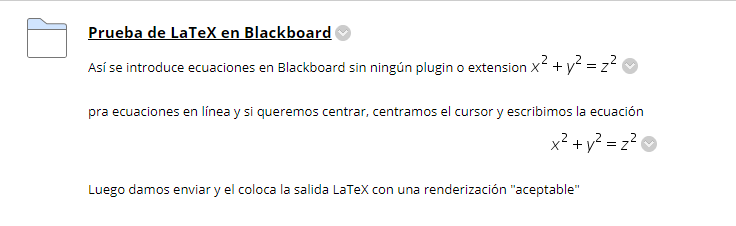
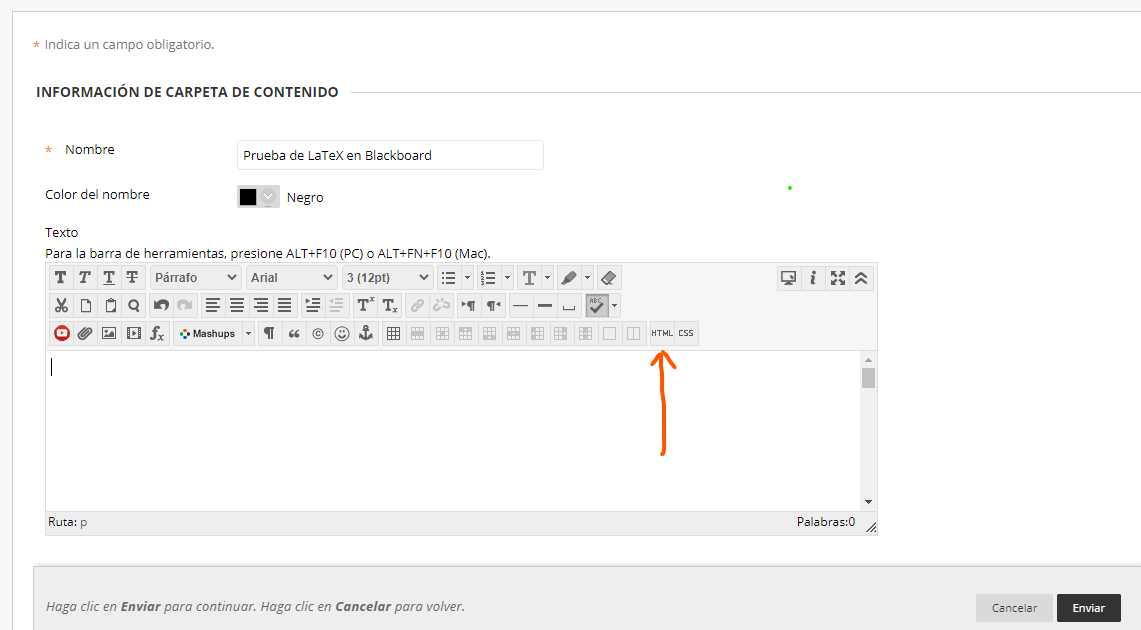
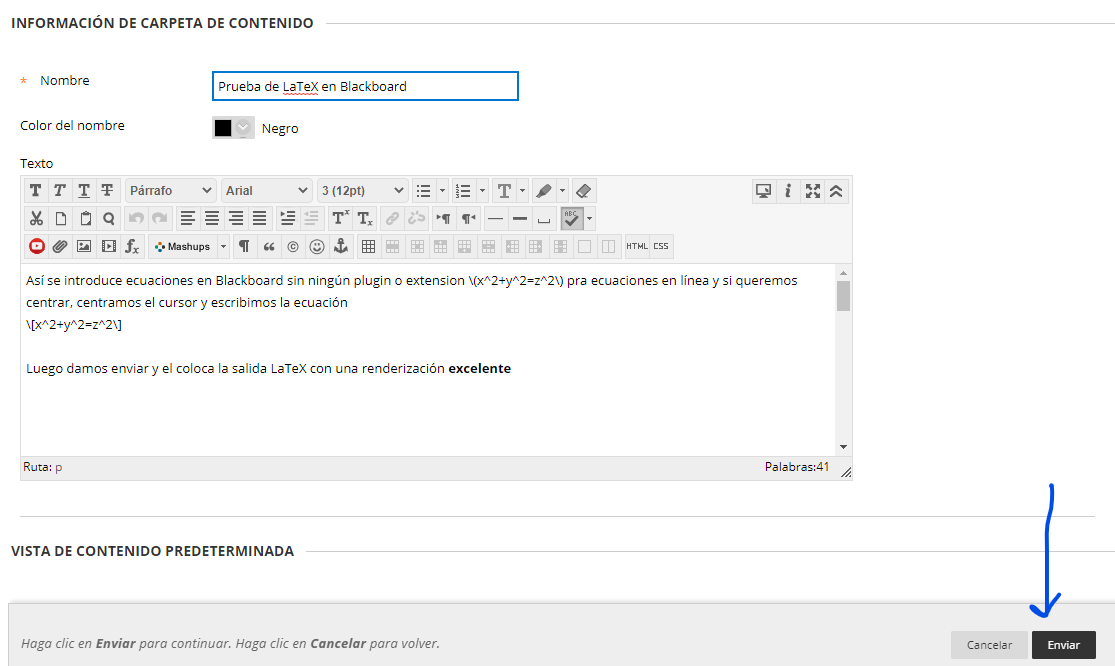
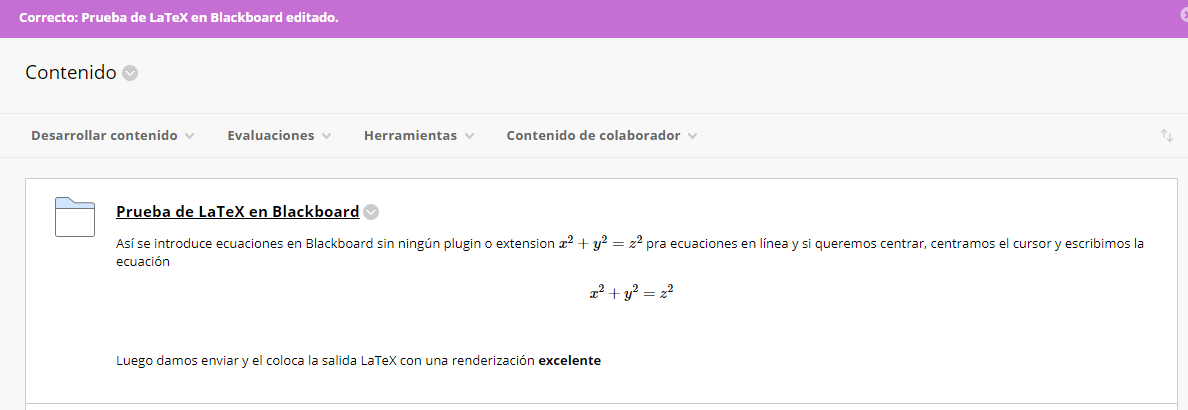
LaTeX in Brightspace
The virtual learning environment Brightspace has a LaTeX editor that is similar to the GeoGebra editor and the simple LaTeX renderer included in this course.
- In any Brightspace text editor, click on the "Show All Components" button (the ellipsis ...)
- Clicking on the Sigma button will show a dropdown with options for equation and symbol insertion.
- You can choose the LaTeX editor from the list.
LaTeX in Google Docs
Google Docs allows you to insert equations into your documents, and provides an equation editor to help you create the mathematics you want. However, if you know a bit of LaTeX, you can speed things up by using the Google Docs Equation Shortcuts, which are essentially LaTeX commands without the curly braces.
Google's official documentation on the use of equation shortcuts is very brief, but one enterprising user has come up with an unofficial cheatsheet.
Once you have finished typing the shortcut, Google Docs will automatically replace it with the symbol, and create editable spaces for you to put any required arguments. For example, typing "\frac" within the equation editing region will cause Google Docs to create a horizontal line, and places for the numerator and denominator.
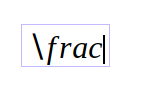
If you have a Google account, try following these steps:
- Open a new Google Doc file.
- From the Insert menu, select Equation.
- In the text area created, type a simple command, like "\alpha" followed by a space.
- Note that your command should be replaced by an appropriate symbol.
LaTeX on any Web Page
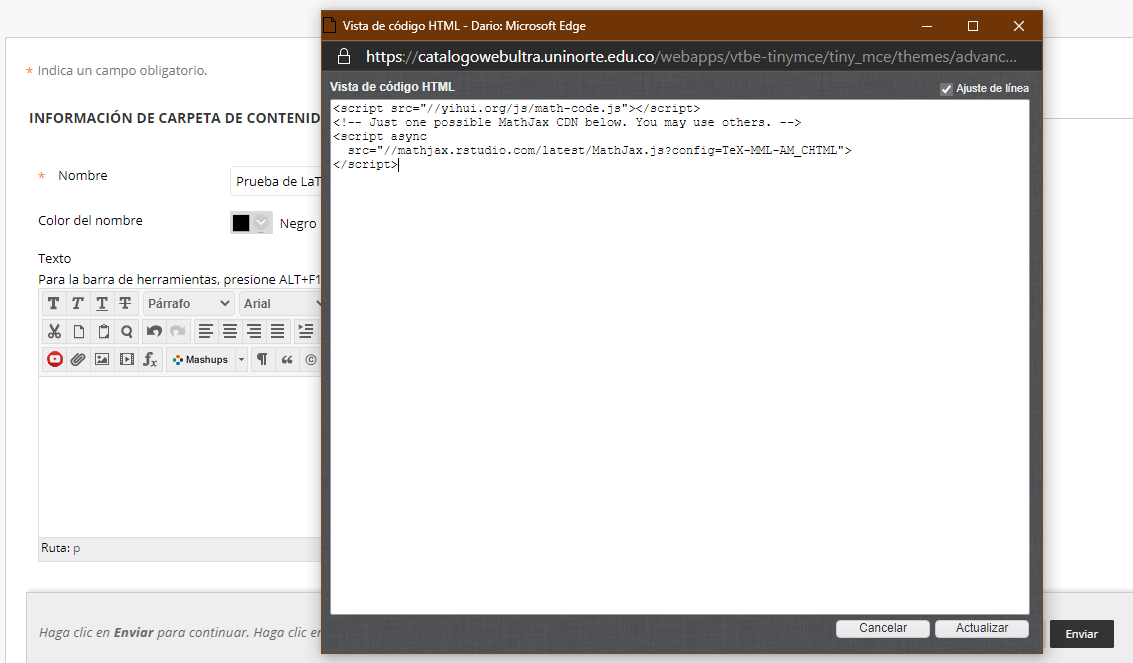
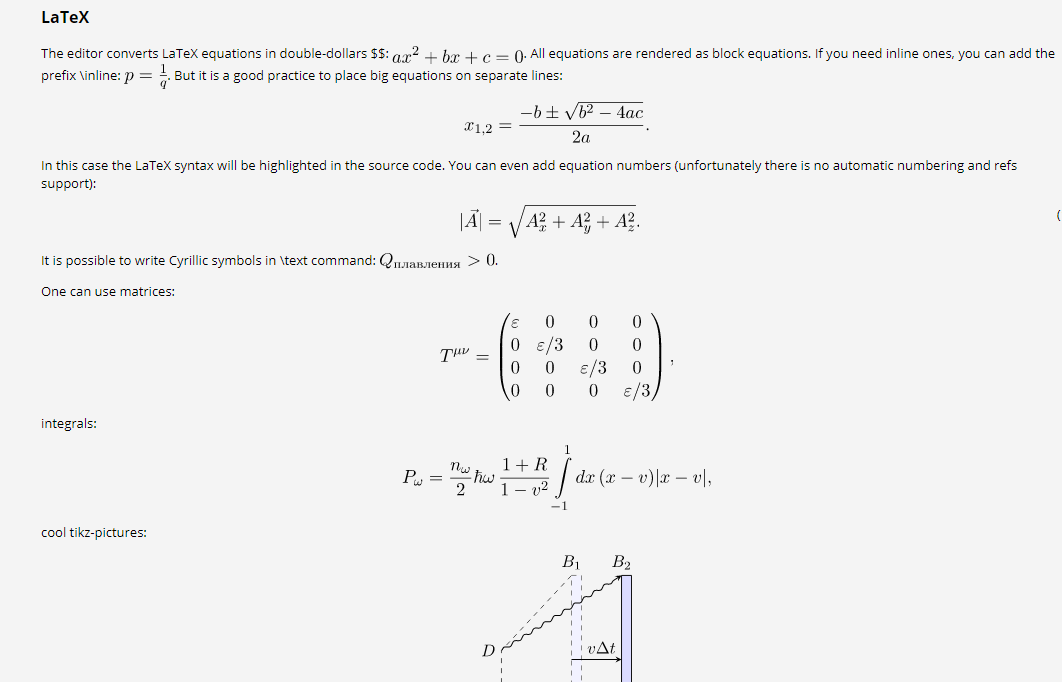
Any webpage can display mathematics using LaTeX thanks to MathJax, a JavaScript library. All of the displayed mathematics in this course is created using LaTeX commands supported by MathJax, so looking at the source for these pages can provide some hints at how it is used.
The MathJax provides instructions on how to include MathJax on any webpage you author. As described there, including a small script will allow you to insert LaTeX formatted math using delimiters: backslashes with round brackets for inline math, and backslashes with square brackets for displayed equations.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width">
<title>MathJax example</title>
<script type="text/javascript" async
src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/mathjax/2.7.5/MathJax.js?config=TeX-MML-AM_CHTML" async>
</script>
</head>
<body>
<p>
When \(a \ne 0\), there are two solutions to \(ax^2 + bx + c = 0\) and they are
\[x = {-b \pm \sqrt{b^2-4ac} \over 2a}.\]
</p>
</body>
</html>
This method can be used on some web-page authoring and blogging platforms that do not offer explicit LaTeX support. If there is a facility for inserting a script, you can insert the MathJax code, and start using LaTeX on your page. This is one way to get LaTeX support on Blogger-based blogs, for example.
MathJax offers support for advanced LaTeX formatting and configuration - please see their docs for more information.
LaTeX in Other Documents
If you are creating a document in another platform that does not have LaTeX support, you can use online LaTeX editors and insert the displayed math as an image file into your document. As described in module 1, editors like CodeCogs, or QuickLaTeX allow you to download a rendered image of your LaTeX commands. Alternatively, you could use the simple LaTeX renderer here and use a screen-capture tool to obtain an image of your equation.
Learn More
Malin Christersson has a nice page about LaTeX on the web, which includes some background, brief descriptions of Wikipedia, Wordpress, and various wiki-engine support for LaTeX, and a short overview of MathJax.
The popular graphing calculator Desmos will automatically render the math you type correctly. But did you know that it uses LaTeX behind the scenes (via another software library, MathQuill), and can even act like a LaTeX editor? In Desmos, type any equation, like "y=sin(theta)", highlight what you typed and copy it into a plain text editor. You will see that the result is a set of LaTeX commands that give the typed math that you see in Desmos. This suggest that if you want to get a bit of LaTeX code but you don't know the commands, you can type it in Desmos and copy the commands from there.